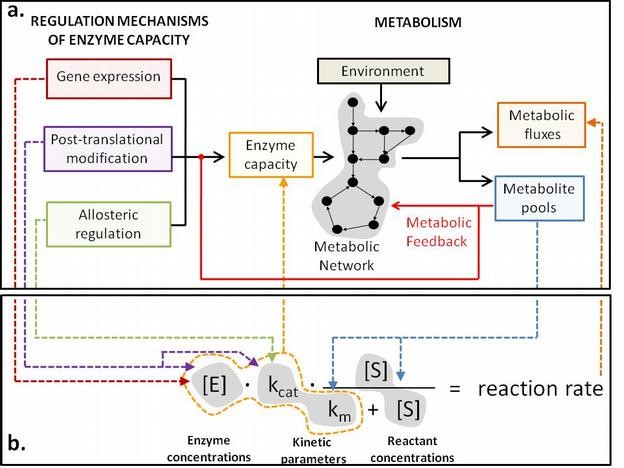
Regulatory protein-metabolite interactions
Regulatory interactions between metabolites and regulatory proteins (transcription factors, kinases) and enzymes trigger and control cell responses, yet this regulatory landscape is largely a terra incognita. Increasing evidence suggests that the majority of proteins bind specific metabolites and that such interactions are relevant to metabolic and gene regulation. In sharp contrast to physical mapping of protein-protein or protein-DNA interactions, there are currently no established methods to systematically identify functional allosteric protein- metabolite interactions.
In various projects, we pursue a combined experimental (often using dynamic metabolomics data) and computational approach to discover in vivo relevance of metabolite-protein interactions and to identify their specific role in the larger regulation scheme. A particular focus is on E. coli and B. subtilis central metabolism and TORC1 signaling in yeast.
References
- Gruber C, Noor E, Sauer U (2025). Systematic identification of allosteric effectors in Escherichia coli metabolism. PNAS. external page https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.2423767122
- Reichling S, Doubleday P, Germade T, Bergmann A, Loewith R, Sauer U & Holbrook-Smith D (2023). Dynamic metabolome profiling uncovers potential TOR signaling genes. eLife. external page https://elifesciences.org/articles/84295
- Ledezma-Tejeida D, Schastnaya E & Sauer U (2021). Metabolism as a signal generator in bacteria. Curr Op Sys Bio, 28, 100404. external page https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coisb.2021.100404
- Chubukov V, Gerosa L, Kochanowski K & Sauer U (2014). Coordination of microbial metabolism. Nature Rev Microbiol. 12:327-40.
- Link H, Christodoulou D & Sauer U (2014). Advancing metabolic models with kinetic information. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 29: 8-14.
- Link H, Kochanowski K & Sauer U (2013). Systematic identification of allosteric protein-metabolite interactions that control enzyme activity in vivo. Nature Biotechnol. 31: 357-61.
- Robitaille AM, Christen S, Shimobayashi M, Cornu M, Fava LL, Moes S, Prescianotto-Baschong C, Sauer U, Jenoe P & Hall MN. Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveal mTORC1 activates de novo pyrimidine synthesis. Science 339:1320-3.
- Gerosa L & Sauer U (2011). Regulation and control of metabolic fluxes in microbes. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 22:566-75.