Software for High-Throughput targeted analysis of SWATH-MS data
IMSB researchers describe an open-source software which allows targeted analysis of SWATH-MS data, a novel type of targeted mass spectrometry first introduced by the Aebersold lab in 2012. The OpenSWATH software allows to increase the number of analyzed peptides in targeted experiments by up to 100-fold (compared to SRM) by leveraging the large amount of data present in a SWATH-MS run
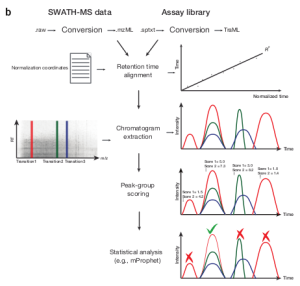
SWATH-MS is a novel mass spectrometric technique that combines the advantages of shotgun proteomics (high throughput) with those of targeted proteomics (high specificity and quantitative accuracy). Previously, proteomics researchers had to choose between the semi-stochastic shotgun acquisition method or the highly reproducible targeted proteomics method which suffered from low throughput. Previously, the Aebersold lab described a method termed SWATH-MS which had the potential to increase the throughput of targeted proteomics substantially. However, at the time no published software was able to handle SWATH-MS data. With this paper, the IMSB researchers present a tool for the automated, targeted analysis of SWATH-MS (data-independent acquisition (DIA)) data.
The authors find that OpenSWATH delivers very high sensitivity at low error rates as well as accurate quantification results. When applied to the analysis of SWATH MS datasets acquired from digested, unfractionated microbial extracts, the software was able to reproducibly quantify over 70% of the expressed proteome of Streptococcus pyogenes and to report over 80 potential virulence factors. This study and multiple other ongoing studies in the Aebersold lab show the unprecedented coverage and reproducibility of the SWATH-MS method which can now be fully exploited using the OpenSWATH software.
Reference: Röst HL, Rosenberger G, Navarro P, Gillet L, Miladinović SM, Schubert OT, Wolski W, Collins BC, Malmström J, Malmström L, Aebersold R. OpenSWATH enables automated, targeted analysis of data-independent acquisition MS data. Nat Biotechnol. 2014 Mar;32(3):219-23. external page DOI